Microgrids: Local, Independent, and Intelligent Energy Systems
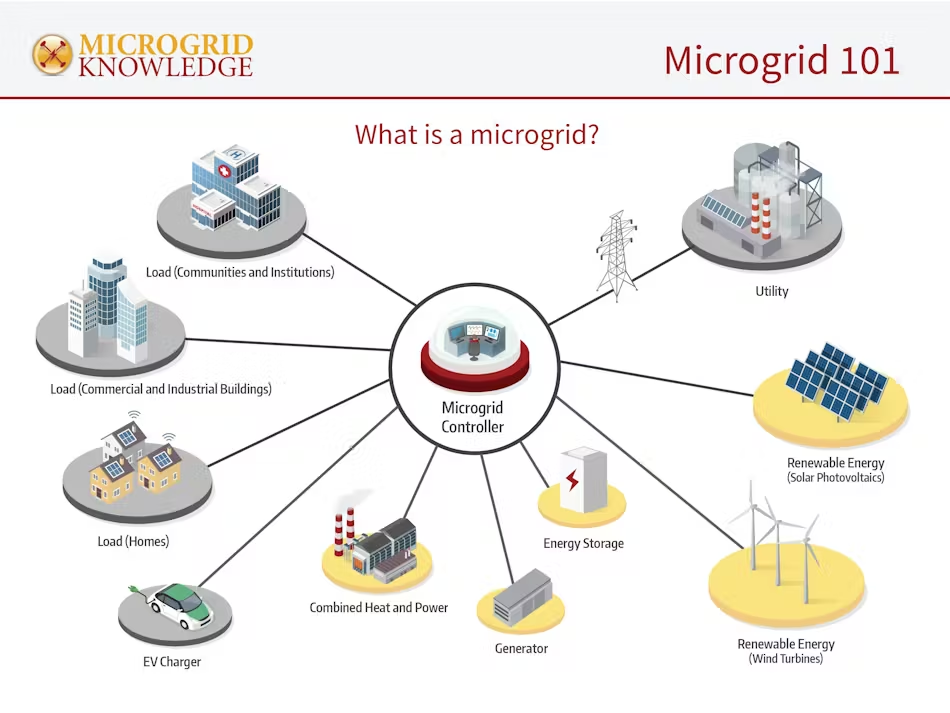
A microgrid is a self-contained energy system that powers a specific area, like a campus, hospital, or neighborhood. It generates energy locally using sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, generators, and batteries, and may also include electric vehicle charging stations.
Key Features
- Local Generation
Microgrids produce energy close to where it’s used, reducing transmission losses of 8–15%, which is common with centralized grids. Power sources, like solar panels, are often located on-site or nearby. - Independent Operation
Microgrids can disconnect (“island”) from the main grid, maintaining power during outages caused by storms or grid failures. While often connected to the central grid for efficiency, they can operate autonomously in remote or unreliable grid areas. - Smart Control
A microgrid’s controller manages energy resources (e.g., solar, batteries) to meet goals like cost savings, clean energy, or reliability. It responds to real-time conditions, like buying cheap grid power or storing solar energy, to optimize efficiency.
By integrating diverse energy sources through advanced algorithms, microgrids deliver reliable, efficient, and sustainable energy solutions.